Automating Clock-Domain Crossing Verification for DO-254 (and Other Safety-Critical) Designs
DO-254 methodologies must ensure that a device is going to behave as specified, and that everything possible is done to catch bugs before the device will be operating in flight. DO-254 projects should use an automated solution such as Questa™ CDC designed specifically for CDC verification to bridge the knowledge gap between design and verification teams, and to ensure comprehensive prevention of this problem.

-
Overview of DO-254
The focus of Document RTCA/DO-254 “Design Assurance Guidance for Airborne Electronic Hardware” (referred to herein as “DO-254”) is hardware reliability for flight safety. In other words, the FAA, EASA and other aviation authorities intend to ensure that the complex electronic hardware used in avionics works reliably as specified, avoiding faulty operation and potential air disasters. DO-254 defines a process that hardware vendors must follow to get their hardware certified for use in avionics. DO-254, which the FAA began enforcing in 2005 (through AC20-152), is modeled after DO-178B, the equivalent process for certifying software, which was published in its original version (DO-178) over 45 years ago. All in-flight hardware (FPGA or ASIC designs) must now comply with DO-254.
NOTE: This document does not provide general information on the DO-254 process but rather focuses on the issue of clock-domain crossing verification and tool assessment, specifically for the tool Questa CDC.
The Problem with Clock-Domain Crossing (CDC)
Metastability is the term used to describe what happens in digital circuits when the clock and data inputs of a flip-flop change values at approximately the same time. This is not a problem in single-clock designs, but this becomes a problem on paths transmitting data between asynchronous clock domains. When the data changes in a flip-flop’s setup/hold window, this leads to the flip-flop output oscillating and settling to a random value, as shown in figure 1. In this case, the output of the flip-flop is said to have gone “metastable” and will lead to incorrect design functionality such as data loss or data corruption on clock-domain crossing (CDC) paths. This situation happens in every design containing multiple asynchronous clocks, which occur any time two or more discrete systems communicate.
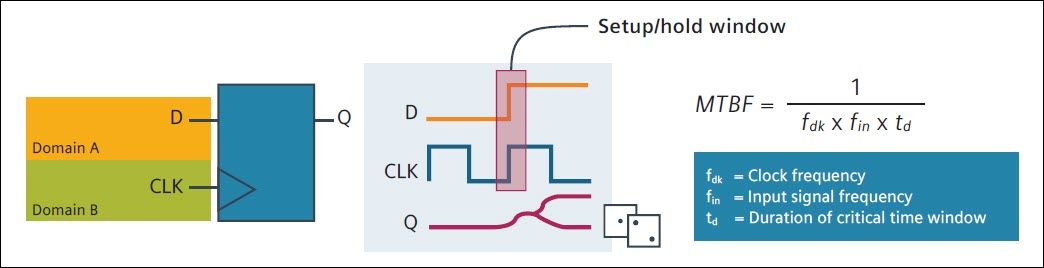
Figure 1: Clock domains, metastability and mean time between failure calculations.
Metastability is a serious problem in safety-critical designs in that it frequently causes chips to exhibit intermittent failures. These failures generally go undetected during simulation (which tests a chip’s logic functions) and static timing (which tests for timing – within a single clock domain). A typical verification methodology simply does not consider potential bugs from clock-domain crossing paths. Thus, if CDC paths are not explicitly verified, CDC bugs are typically identified in the actual hardware device in the field. For DO-254 projects, catching faulty operation “in the field” means critical bugs may not be caught until an in-flight failure.
With today’s highly integrated and concurrent designs, the number of independent clock domains found on the typical device is growing. According
to an industry research study performed by the Wilson Research Group in 2022, 93 percent of IC/ASIC designs contained two or more asynchronous clock domains. This means that the probability of metastability bugs has grown substantially from previous designs.The real issue is that traditional simulation and timing analysis do not accurately analyze multi-clock designs. Designers are generally aware of the metastability problem and try to implement logic to isolate the outputs of the metastable registers such that this metastable value does not propagate into the rest of the design. For example, experienced designers add synchronizers between clock domains, create protocols for transferring data between domains, and try to avoid situations where data from multiple clock domains reconverge, as shown in figure 2.
-
Download Paper
-
Automating Clock-Domain Crossing Verification for DO-254 (and Other Safety-Critical) Designs
Functional Safety Sep 10, 2025 pdf
-