@MichaelP
Thanks. Yes. I know there are a lot of other ways to sync static module world and UVM class dynamic world. For example, interface usage as you suggested. Besides, via uvm_event in config DB, or simply putting SV event in static places like global area or packages. uvm_event_pool may be another way. uvm_wait_for_naba_region() is also one way.
My question is - do you really need to implement what you’re attempting here?
Or might you be overcomplicating it?
Yes. It is really necessary. In reality, mixture of static TB components and UVM class base TB is quite common. Typical example is conventional module based BFM usage with UVM. We usually don’t intend to make a lot of efforts to convert existing assets to UVM class based components. In such case, syncing module based components and UVM phases is the easiest way. Moreover, uvm_wait_for_nba_region() usage is the best practice so far.
But I also know it is originally not for that purpose. That’s why I am searching for better and more decent way.
Anyhow, I did the following experiment.
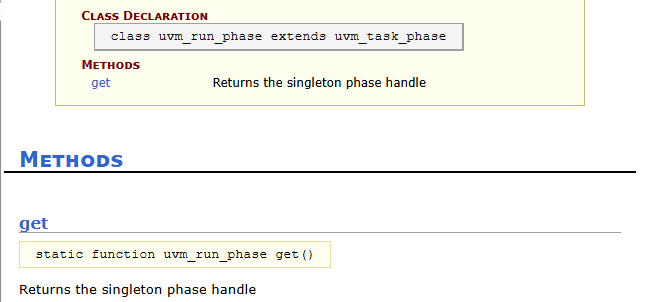
uvm_run_phase::get() usage in TB module, run_phase() task, main_phase() tasks and their comparison with phase in each tasks’ argument.- run_phase() done wait in main_phase() in UVM test class.
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
module tb;
import uvm_pkg::*;
class my_test extends uvm_test;
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
`uvm_component_utils(my_test)
virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_info(this.get_type_name(), "Run Phase", UVM_MEDIUM)
`uvm_info(this.get_type_name(), $sformatf(" phase(%s) : %h %p\n%s",phase.get_full_name(),phase,phase.get_state(),phase.sprint()), UVM_MEDIUM)
begin
uvm_run_phase run_phase = uvm_run_phase::get();
`uvm_info(this.get_type_name(), $sformatf("run_phase(%s) : %h %p\n%s",run_phase.get_full_name(),run_phase,run_phase.get_state(),run_phase.sprint()), UVM_MEDIUM)
end
phase.raise_objection(this, "Starting Run Phase");
#100ns;
phase.drop_objection (this, "Ending Run Phase");
endtask
virtual task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_info(this.get_type_name(), "Main Phase", UVM_MEDIUM)
`uvm_info(this.get_type_name(), $sformatf(" phase(%s) : %h %p\n%s",phase.get_full_name(),phase,phase.get_state(),phase.sprint()), UVM_MEDIUM)
phase.raise_objection(this, "Starting Main Phase");
begin
uvm_run_phase run_phase = run_phase = uvm_run_phase::get();
`uvm_info(this.get_type_name(), $sformatf("run_phase(%s) : %h %p\n%s",run_phase.get_full_name(),run_phase,run_phase.get_state(),run_phase.sprint()), UVM_MEDIUM)
run_phase.wait_for_state(UVM_PHASE_DONE);
end
#100ns;
phase.drop_objection (this, "Ending Main Phase");
endtask
endclass
initial run_test("my_test");
initial begin
uvm_pkg::uvm_run_phase run_phase;
run_phase = uvm_pkg::uvm_run_phase::get();
`uvm_info("TB", "module initial begin", UVM_MEDIUM)
`uvm_info("TB", $sformatf("run_phase(%s) : %h %p\n%s",run_phase.get_full_name(),run_phase,run_phase.get_state(),run_phase.sprint()), UVM_MEDIUM)
run_phase.wait_for_state(UVM_PHASE_STARTED);
`uvm_info("TB", "Waited for Run Phase Start", UVM_MEDIUM)
end
endmodule;
The result is quite interesting.
UVM_INFO tb.sv(46) @ 0: reporter [TB] module initial begin
UVM_INFO tb.sv(47) @ 0: reporter [TB] run_phase(run) : 00007f72856dce00 UVM_PHASE_UNINITIALIZED
--------------------------------
Name Type Size Value
--------------------------------
run uvm_run_phase - @170
--------------------------------
UVM_INFO tb.sv(15) @ 0: uvm_test_top [my_test] Run Phase
UVM_INFO tb.sv(16) @ 0: uvm_test_top [my_test] phase(common.run) : 00007f72856dcc00 UVM_PHASE_EXECUTING
----------------------------
Name Type Size Value
----------------------------
run <unknown> - @172
----------------------------
UVM_INFO tb.sv(19) @ 0: uvm_test_top [my_test] run_phase(run) : 00007f72856dce00 UVM_PHASE_UNINITIALIZED
--------------------------------
Name Type Size Value
--------------------------------
run uvm_run_phase - @170
--------------------------------
UVM_INFO tb.sv(27) @ 0: uvm_test_top [my_test] Main Phase
UVM_INFO tb.sv(28) @ 0: uvm_test_top [my_test] phase(uvm.uvm_sched.main) : 00007f72855fb600 UVM_PHASE_EXECUTING
----------------------------
Name Type Size Value
----------------------------
main <unknown> - @113
----------------------------
UVM_INFO tb.sv(32) @ 0: uvm_test_top [my_test] run_phase(run) : 00007f72856dce00 UVM_PHASE_UNINITIALIZED
--------------------------------
Name Type Size Value
--------------------------------
run uvm_run_phase - @170
--------------------------------
UVM_FATAL uvm_phase_hopper.svh(587) @ 9200000000000: reporter [PH_TIMEOUT] Default timeout of 9200000000000 hit, indicating a probable testbench issue
- The instance of
uvm_run_phase::get() and phase argument of run_phase() task are different.
- The instance of
uvm_run_phase::get() is same in TB module and UVM class.
uvm_run_phase::get().wait_for_state() doesn’t work even in UVM class (timeout in main_phase()).
I wonder what wait_for_state() is for…  I looks it is useless even in UVM class. I originally thought it is for UVM phase sync in static modules since it is static. It doesn’t need to be static if it is not used in modules. I really wonder why it is static…
I looks it is useless even in UVM class. I originally thought it is for UVM phase sync in static modules since it is static. It doesn’t need to be static if it is not used in modules. I really wonder why it is static…
This might be kind of a bug of UVM.