Can anyone explain in detail regarding BFM?
In reply to p_patel:
Search: Bus Functional Model
In reply to p_patel:
Can anyone explain in detail regarding BFM?
What exactly are you looking for in a Bus Functional Model, which is a software reflection of a nus interface that interacts with your DUT?. In general, there are several aspects to the design of a BFM:
- FUNCTIONALITY: This is the emulation of the units that are on the other side of the DUT. This could be a driver with a source of stimuli if the DUT is a slave. This could also be a slave set of responses if the DUT is a master. A BFM is also involved with other functions such as error injection and verification, which can be implemented as a design apart from the BFM. But the term BFM is often very generic and can refer to anything that is outside the DUT.
- ERROR INJECTION: Needed to check DUT’s responses and recovery from bus errors.
- VERIFICATION: Needed to alert the verification engineer of DUT errors and to provide test coverage. Assertions can help in this endeavor.
In my latest book SystemVerilog Assertions Handbook 4th Edition, 2016 I address not only the use of assertions for verification, but also the use of SystemVerilog for the generation of constrained random testing to verify assertions or to drive a DUT. See Chapter 9 in http://systemverilog.us/sva4_preface.pdf for TOC.
Ben Cohen
http://www.systemverilog.us/ ben@systemverilog.us
- SystemVerilog Assertions Handbook 4th Edition, 2016 ISBN 978-1518681448
- A Pragmatic Approach to VMM Adoption 2006 ISBN 0-9705394-9-5
- Using PSL/SUGAR for Formal and Dynamic Verification 2nd Edition, 2004, ISBN 0-9705394-6-0
- Real Chip Design and Verification Using Verilog and VHDL, 2002 isbn 0-9705394-2-8
- Component Design by Example ", 2001 ISBN 0-9705394-0-1
- VHDL Coding Styles and Methodologies, 2nd Edition, 1999 ISBN 0-7923-8474-1
- VHDL Answers to Frequently Asked Questions, 2nd Edition ISBN 0-7923-8115
Could u please explain a difference of BFM and VIP?
I am not sure, but as per my understanding, VIP = scenario generator + BFM
In reply to bdreku:
Could u please explain a difference of BFM and VIP?
I am not sure, but as per my understanding, VIP = scenario generator + BFM
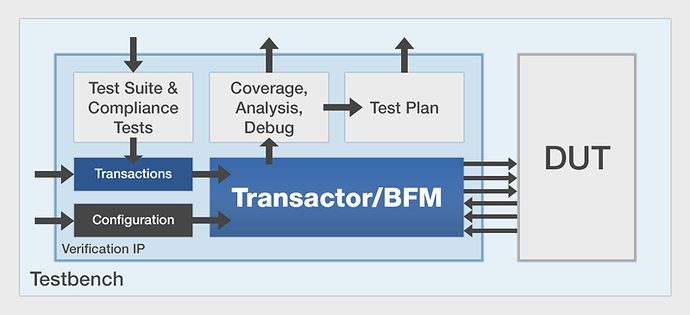
This site provides a good explanation and shows the architecture of a VIP
If you look at
you’ll see that a BFM is a model of the interface to the DUT. The VIP includes, besides the BFM, the test environment to allow the user to integrate his DUT and verify that the DUT’s interface (e,g,Ethernet) does meet the specs for that bus. If you don’t have a packaged VIP, then you would have to create one yourself. Specifically, you would need to fully understand the interface, define a test plan, write a test suite, define a BFM that accepts the commanded transactions (e.g., read/writes) and responds to the DUT. You must also provide the verification that the DUT does indeed meet the interface requirement per specs (e.g., the Ethernet spec). It is a LOT OF WORK! For standard protocols, buying a VIP is faster, and could even be cost effective.
Ben Cohen
http://www.systemverilog.us/ ben@systemverilog.us
- SystemVerilog Assertions Handbook 4th Edition, 2016 ISBN 978-1518681448
- A Pragmatic Approach to VMM Adoption 2006 ISBN 0-9705394-9-5
- Using PSL/SUGAR for Formal and Dynamic Verification 2nd Edition, 2004, ISBN 0-9705394-6-0
- Real Chip Design and Verification Using Verilog and VHDL, 2002 isbn 0-9705394-2-8
- Component Design by Example ", 2001 ISBN 0-9705394-0-1
- VHDL Coding Styles and Methodologies, 2nd Edition, 1999 ISBN 0-7923-8474-1
- VHDL Answers to Frequently Asked Questions, 2nd Edition ISBN 0-7923-8115
In reply to ben@SystemVerilog.us:
Got it. Thank you, Ben. :-)