What are race around conditions and Metastability conditions in System verilog?With Examples anyone please suggest me
In reply to truptipatro:
What are race around conditions and Metastability conditions in System verilog?With Examples anyone please suggest me
Your question is not clear. On race conditions, are you asking:
- Why there are race conditions in SystemVerilog?
- Provide examples of race conditions?
- What are ways to overcome race conditions?
On metastability, are you asking:
- What is metastability?
- Examples of metastability?
- Ways to overcome metastability?
Ben Cohen
http://www.systemverilog.us/ ben@systemverilog.us
- SVA Handbook 4th Edition, 2016 ISBN 978-1518681448
- A Pragmatic Approach to VMM Adoption 2006 ISBN 0-9705394-9-5
- Using PSL/SUGAR for Formal and Dynamic Verification 2nd Edition, 2004, ISBN 0-9705394-6-0
- Real Chip Design and Verification Using Verilog and VHDL, 2002 isbn 0-9705394-2-8
- Component Design by Example ", 2001 ISBN 0-9705394-0-1
- VHDL Coding Styles and Methodologies, 2nd Edition, 1999 ISBN 0-7923-8474-1
- VHDL Answers to Frequently Asked Questions, 2nd Edition ISBN 0-7923-8115
In reply to ben@SystemVerilog.us:
Yes my questions are :
- Why there are race conditions in SystemVerilog with examples ?
- What is metastability and examples of this?
In reply to truptipatro:
In reply to ben@SystemVerilog.us:
Yes my questions are :
- Why there are race conditions in SystemVerilog with examples ?
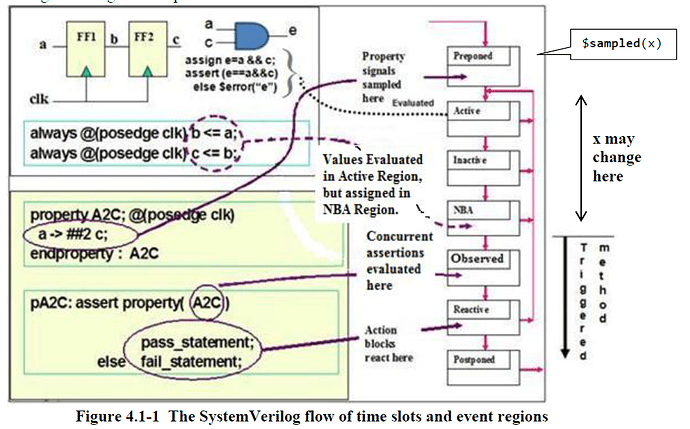
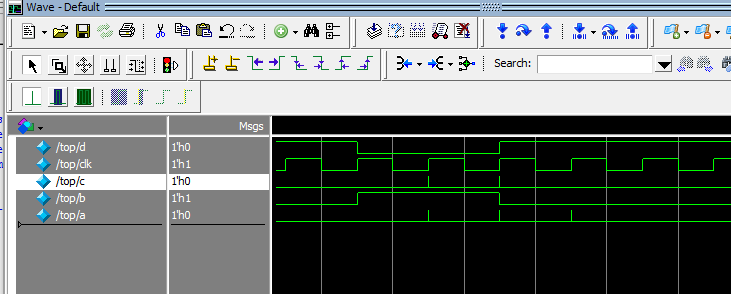
SystemVerilog has evaluation regions, as shown below (extracted from my SVA Handbook). This causes glitches within and evaluation time step, as the simulator goes through these various phases, depending upon the type of signals being evaluated. Below is a simulation model and results
import uvm_pkg::*; `include "uvm_macros.svh"
module top;
bit clk, a, b, c, d;
default clocking @(posedge clk); endclocking
initial forever #10 clk=!clk;
always_comb begin
c = a && b;
b = !d;
end
always_ff @(posedge clk) begin
automatic bit va, vd;
if (!randomize(a, vd) with
{ va dist {1'b1:=1, 1'b0:=3};
vd dist {1'b1:=2, 1'b0:=1};
}) `uvm_error("MYERR", "This is a randomize error")
a <= va;
d <= vd;
end
endmodule
- What is metastability and examples of this?
I explain metastability in my real Chip design and Verification book.
For your convenience, I am giving a few pages on that topic at
Ben Cohen
http://www.systemverilog.us/ ben@systemverilog.us
- SVA Handbook 4th Edition, 2016 ISBN 978-1518681448
- A Pragmatic Approach to VMM Adoption 2006 ISBN 0-9705394-9-5
- Using PSL/SUGAR for Formal and Dynamic Verification 2nd Edition, 2004, ISBN 0-9705394-6-0
- Real Chip Design and Verification Using Verilog and VHDL, 2002 isbn 0-9705394-2-8
- Component Design by Example ", 2001 ISBN 0-9705394-0-1
- VHDL Coding Styles and Methodologies, 2nd Edition, 1999 ISBN 0-7923-8474-1
- VHDL Answers to Frequently Asked Questions, 2nd Edition ISBN 0-7923-8115