//I am wondering if there is a simple way to test this kind of situation:
if <sequence> then
OUTPUT==1
else
OUTPUT==0
//or basically, what is desiredL
p_1 : assert property (
not <sequence> |-> OUTPUT == 0); // ILLEGAL CONSTRUCT
This is a bit tricky, but it is possible to do using the implies or the**|->** operators and the sequence endpoint, i.e., the .triggered. The implies can be used if the antecedent is a property instead of a sequence
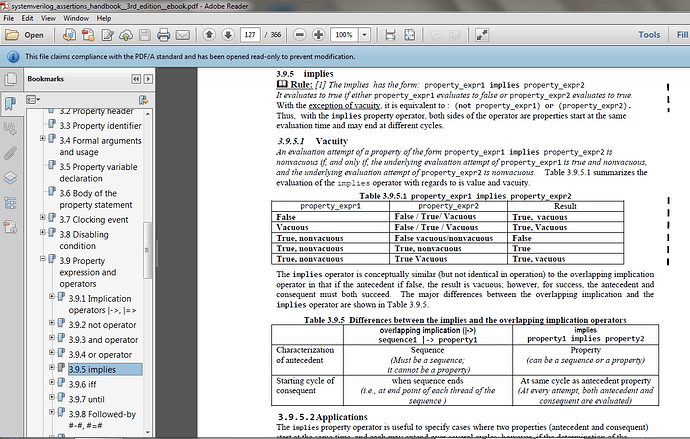
I explain the implies in my book, and I am making an image of that page in
Take particular attention to table Table 3.9.5.1
property_expr1 implies property_expr2.
Specifically in
p1 implies p2, both p1 and p2 start at the same cycle, and if p1 is false, then the property is vacuous. but if p1 is true, then p2 must be true.
Below is an an example of the solution:
The simulation waveform is at
http://systemverilog.us/nosequence.png
Code is at
module notsq;
bit clk, out1, a, b, ab_endpt;
sequence q_ab;
@(posedge clk) a ##1 b;
endsequence
ap_notsq: assert property(@(posedge clk)
!out1 implies not(q_ab.triggered));
ap_notsq2: assert property(@(posedge clk)
!out1 |-> not(q_ab.triggered));
initial forever #10 clk=!clk;
always @(posedge clk) begin : p2
if (!randomize(a, b, out1)) $error();
end : p2
endmodule
Also, from my book on the iff
3.9.6 iff
Rule: [1] The iff property has the following form: property_expr1 iff property_expr2
At every clocking event, there is an evaluation attempt of the iff property that consists of the LHS property expression and the RHS . The RHS and LHS properties are started concurrently and may finish at different times. For an evaluation attempt to be successful, both sides must either evaluate to true or both sides must evaluate to false.
Equivalence: (p1 iff p2) // is equivalent to
((p1 implies p2) and (p2 implies p1)
Ben Cohen
http://www.systemverilog.us/ ben@systemverilog.us
- SystemVerilog Assertions Handbook 3rd Edition, 2013 ISBN 878-0-9705394-3-6
- A Pragmatic Approach to VMM Adoption 2006 ISBN 0-9705394-9-5
- Using PSL/SUGAR for Formal and Dynamic Verification 2nd Edition, 2004, ISBN 0-9705394-6-0
- Real Chip Design and Verification Using Verilog and VHDL, 2002 isbn 0-9705394-2-8
- Component Design by Example ", 2001 ISBN 0-9705394-0-1
- VHDL Coding Styles and Methodologies, 2nd Edition, 1999 ISBN 0-7923-8474-1
- VHDL Answers to Frequently Asked Questions, 2nd Edition ISBN 0-7923-8115